Test Your Skills
Each month Fluid Power Journal brings you an industry problem with a solution the following month.
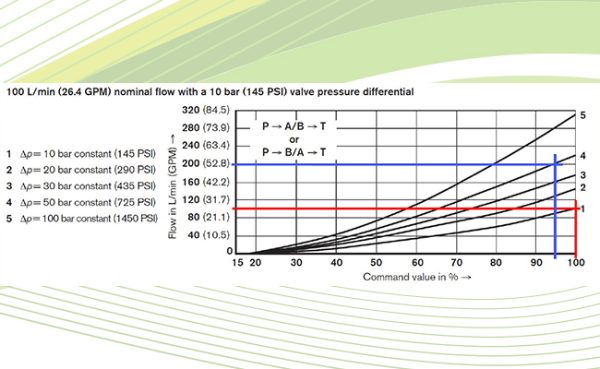
Test Your Skills: Application of Proportional Valves
There are many applications for proportional solenoids in the control of hydraulic pressure and flow in both mobile and industrial applications. The terms …
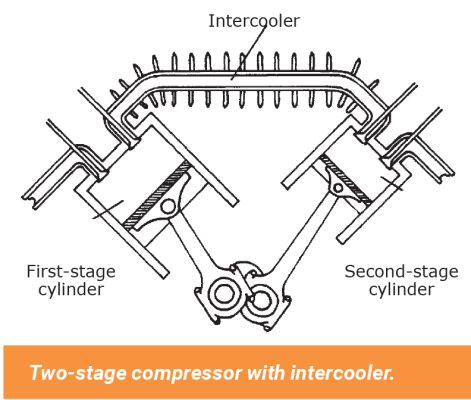
Test Your Skills: Types and Applications of Compressors
The generic term “supply side” is often used to refer to the complete package that includes the compressor, drive motor, and associated hardware, as well …
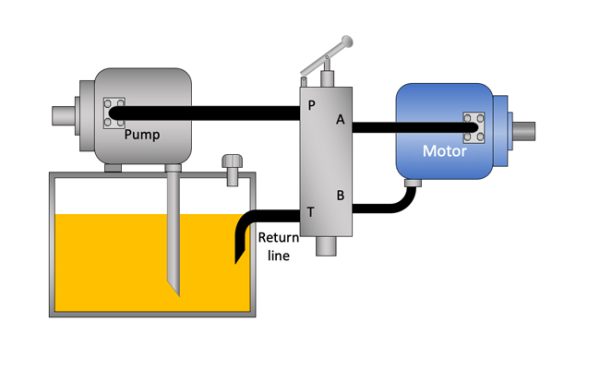
Test Your Skills: Hydrostatic Transmissions
The transmission of force through a contained hydraulic fluid (hydrostatics) will fall into one of two categories: open circuit or closed circuit. An open …
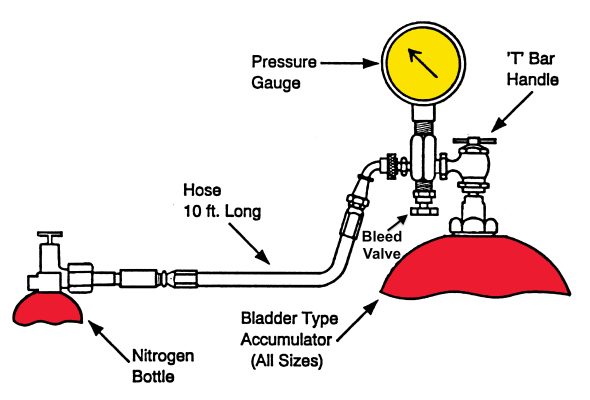
Gas-Charged Hydraulic Accumulators
Accumulators are pressure vessels and are subject to the American Society of Testing Materials standards in addition to the International Standards …
Stopping a Load with a Shock Absorber
It is common practice to position shock absorbers to cushion loads attached to air cylinders, rather than to subject the air cylinders to shock loading …
Recognizing Misaligned Cylinders
Misalignment of a cylinder occurs when the load is not applied along the centerline of the rod. Many applications have a small amount of inherent misalignment …
Linear Displacement Sensors
The first factors to consider when selecting linear displacement sensors are the mechanical interface, dimensions, contact, noncontact, and environmental …
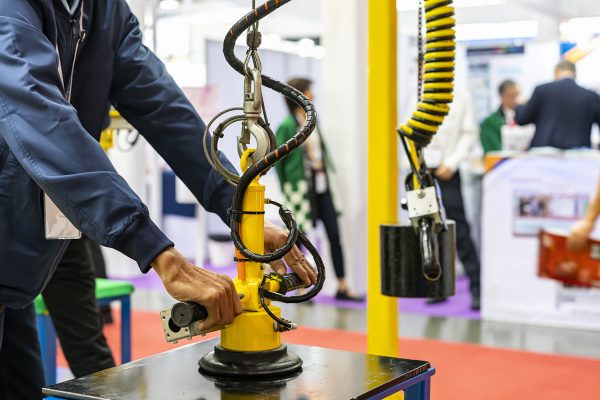
Selecting Vacuum Pads
Vacuum pads are primarily used for handling smooth surfaced material but can be used with textured or irregular shaped material as well. Because sheet glass …
The Function of Fluids
The word “fluid” refers to something that flows and can describe a gas or a liquid. A hydraulic system is the transmission of power by means of a …
Understanding Supply-Side Air Preparation
As air is compressed, the temperature of the air increases significantly. The compressor discharge air temperature is typically over 200°F (93°C) for a …