Enabling IIoT Connectivity for Industry 4.0

By Will Healy III, Industry Marketing Director, Balluff Inc.
The next industrial revolution isn’t coming; it has already begun. The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and Industry 4.0 applications are the required cost of admission to be competitive in manufacturing today, regardless of whether a business is “mechanical only” or not. And to stay viable,
businesses must be willing to invest in and efficiently optimize their own production through the use of both.
Industrial Internet of Things
Stated simply, IIoT is about connecting devices on the plant floor to a network. These connections deliver new ways to generate and collect useful data. By providing visibility down into the machine, IIoT allows for significant improvements to productivity and quality, including more predictive maintenance and big data analytics.
With IIoT, we are able to improve overall equipment effectiveness and provide new insights into our business.
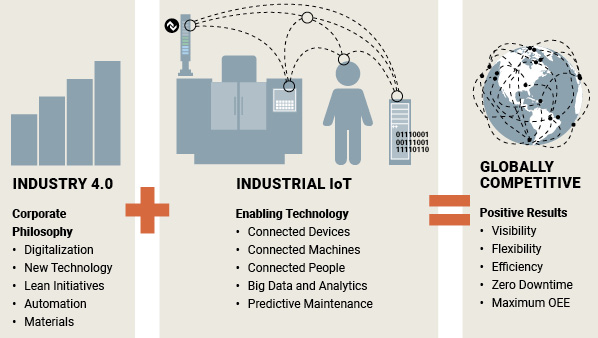
Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 aims to achieve unprecedented flexibility, efficient production, and visibility at every level of production through a blend of digitalization, new technology, and practical decisions meant to improve manufacturing. The impact of Industry 4.0 can be felt throughout our processes and across the supply chain. It blends lean initiatives, automation, technology, materials, downtime reduction upgrades, and investments in overall equipment effectiveness. This philosophy keeps the current generation of manufacturers competitive in a global market. While the German government set this precedent for Industry 4.0, the entire manufacturing world must now take on this challenge.
Implementing IIoT and Industry 4.0
By becoming IIoT-ready, standard systems like hydraulic power units (HPUs) receive a major boost. Traditional on/off flow or pressure switches can be upgraded to provide information beyond the simple switch points. Additionally, analog devices like temperature, pressure, flow, and level transducers can become IIoT-ready through open standard technologies like IO-Link. These technologies add significant value by incorporating easy-to-report parameters, diagnostics, events and warnings. A standard HPU can become a smart power unit with minimal modification.
The value of IIoT increases with predictive maintenance, remote monitoring, and ease of troubleshooting. With IIoT-ready technologies, we can connect to the devices and know exactly what needs fixing. In addition, it provides the possibility of predicting the failure before it occurs. This can dramatically reduce machine downtime as well as the time spent in hazardous locations.
It isn’t enough to merely select IIoT-ready technologies to fully leverage the value of Industry 4.0. It is imperative that businesses analyze processes and implement flexibility into production. It is necessary to determine where automation technology makes sense to support lean processes. Manufacturers can see into every aspect of their production while manufacturing hundreds of variations of product in the same line, all while assuring quality standards with virtually zero machine downtime.
The difference between Industry 4.0 and IIoT
IIoT connects our devices, our data, our machines, and our people to the advantage of our company and customers. IIoT’s connectivity is an enabling force for Industry 4.0., and Industry 4.0 is a cultural philosophy about how we can use that increased visibility, flexibility, and efficiency to be more competitive. Only by embracing both can businesses today sustain global competitiveness and achieve the highest levels of success.
About the Author:
Will Healy III is the Industry Marketing Director at Balluff Inc. in Florence, Kentucky, and he is enthusiastic about smart manufacturing, automation, and STEM education. Healy graduated from Purdue University with a degree in mechanical engineering, and has been sharing his passion for automation for more than 10 years in a variety of industries. He is published and quoted in various trade magazines, works as an industrial adviser for multiple universities, and has widely presented on the value sensors, networking, and IIoT bring to manufacturing.