Pneumatic Cylinders and Actuators for Modern Conveyor & ASRS Systems
By Shannon Winkler, National Sales Manager, Compact Automation Products
Since the invention of conveyor systems more than 125 years ago, their primary function has remained the same: moving parts, materials, and products from one location to another. Originally developed for use in the mining industry, conveyor systems have continuously evolved over the years and serve as an essential component for many manufacturing and production operations across multiple industries.
Today, these industries include original equipment manufacturers of food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and electronics manufacturing equipment, along with packaging equipment, industrial equipment, robotics, and more. Additional areas where conveyor systems can be found include mail and package sorting, logistics, distribution and parcel delivery centers, and airport baggage handling.
In an automation-driven manufacturing environment, conveyor systems offer many capabilities beyond their original purpose of transporting items. They provide critical functions for meeting manufacturing needs and requirements. Automated capabilities provided by conveyor systems include inspection and testing, lifting and positioning, picking and placing, packaging, and palletizing.
Through these and other automated actions, conveyor systems play a significant role in improving manufacturing efficiencies, minimizing product damage, and enhancing worker safety. Accomplishing these and other manufacturing outcomes, as objects move through a conveyor system, requires precise control and movement enabled by pneumatic and hydraulic actuators and related components. This article provides an overview of these pneumatic cylinders and actuators for conveyor systems and other material handling systems, as well as other applications.
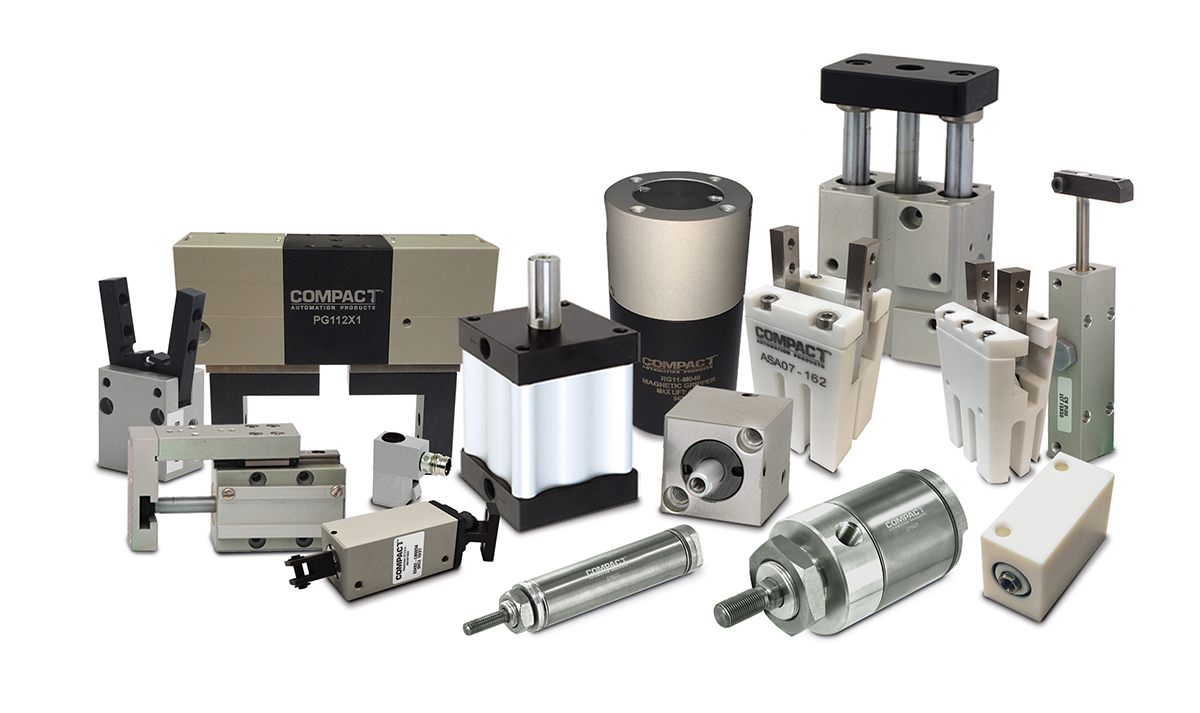

Photo courtesy of Compact Automation Products
Types of Pneumatic Products
Pneumatic cylinder products are mechanical devices powered by compressed air to convert energy into linear or rotary motion Air cylinders are simple to install and maintain, employing a simplistic structure comprised of a cylindrical housing, a piston, and a piston rod. The compressed air is directed into the cylinder, causing the piston to move and creating linear motion. This motion is utilized in tasks such as clamping, lifting, sorting, and object pushing.
The two main types of pneumatic cylinders are single-acting and double-acting, differentiated by their actuation mechanism. Single-acting cylinders exert force in one direction utilizing compressed air and an internal spring or external load to exert force in the opposite direction. Double-acting cylinders exert force in both directions utilizing compressed air.
There are several types of pneumatic cylinders and actuators that offer different functionalities to suit various industrial applications, including conveyor systems. These include:
- Piston-Style Units, which can reliably convert energy from compressed air into linear motion and are capable of handling heavy loads. They are versatile and commonly used in applications that require high force and precision.
- Diaphragm-Style Pneumatic Actuators, which use a flexible diaphragm to generate linear motion. These are ideal for applications that require a compact design and high sensitivity. Diaphragm-style actuators are often used in industries where cleanliness and hygiene are crucial, such as food processing, medical device manufacturing and pharmaceuticals.
- Rotary Actuators are designed to provide semi-rotational motion and are commonly used in applications that require valves or other components to be rotated. Rotary actuators are known for their precise control and ability to handle heavy loads.
- Pneumatic Motors provide continuous rotational motion, operating either clockwise or counterclockwise. They can be used in place of electric motors in some hazardous locations.
Components of Pneumatic Cylinders
Key components of pneumatic cylinder products include the cylinder body, piston, and rod. The cylinder body acts as the main housing while the piston converts compressed air into linear motion. A rod, connected to the piston, extends or retracts to move the load from one point to another based on the specific application requirements.
Pneumatic cylinder components come in various designs and configurations, including those from Compact Automation, are available in round, square, compact, rod-less, and tandem versions. Factors such as operating pressure, force and speed requirements, environmental conditions, and space constraints should be considered when determining the right type of cylinder that is to be selected for any given application.
Sealing elements such as O-rings or lip seals prevent air leakage and protect the internal components from contaminants, such as dirt and debris. Enhancements to air cylinders can be made through various accessories and add-ons like cushioning devices, position sensors, mounting brackets, clevises, or flow control valves.
Pneumatic Cylinder Applications
Key applications where pneumatic cylinders play a crucial role include:
- Industrial Automation: Pneumatic cylinders are commonly used to control the movement of components such as valves, gates, and stoppers in manufacturing facilities. They provide precise and quick movement, making them ideal for applications that require high-speed automation.
- Process Control Systems: Pneumatic cylinders can aid in regulating the flow of fluids and gases in pipelines. By controlling the opening and closing of valves, pneumatic actuators ensure the smooth operation of processes in industries such as refineries, oil and gas, chemical, and pharmaceutical.
Components of Rotary Actuators
Rotary vane actuator components, also known as pneumatic rotary actuators such as those produced by Compact, are mechanical devices that convert energy into rotary motion. They serve as key components in controlling and operating a variety of equipment across industries. The basic structure of an actuator includes a secure housing that encapsulates the rotor with vanes and an output shaft. The rotor is strategically placed within the housing and connected to the output shaft, imparting the rotary motion to the desired mechanism.
Working on the principle of positive displacement, the rotary actuator uses pressure applied on the vanes to create a seal against the housing, splitting it into separate chambers. As the rotor revolves, the volume of each chamber changes, leading to the movement of the vanes.
Rotary Actuator Applications
Rotary actuators play a crucial role in various industries, providing efficient and reliable motion control. Here are some of their key applications:
- Industrial Automation: In assembly lines, manufacturing plants, and other industrial processes, rotary vane actuators are used for their precise and controlled movement. They provide high torque, smooth operation, and longevity, making them an ideal choice for demanding industrial applications.
- Material Handling Systems: These actuators are key components in material handling systems, providing efficient motion control for conveyors, lifts, and other equipment. They can handle heavy loads, ensuring smooth and precise movement of materials in warehouses and logistics facilities.
- Robotic Applications: Rotary vane actuator products are often integrated into robots to provide accurate and smooth movements, thereby enhancing their performance and productivity.
Considerations When Selecting a Rotary Vane Actuator
Choosing the right rotary vane actuator involves several key factors. To start, it’s important to understand the specific requirements of an application such as degrees of rotation, load capacity, torque output, and speed requirements. These factors will guide the selection of the right size and type of actuator.
Key specifications such as maximum operating pressure, temperature range, and mounting options are also critical when selecting the correct rotary vane actuator. It’s necessary to ensure that the actuator can withstand the operating conditions of the application and can be easily integrated into an existing system.
Installation and Maintenance of Pneumatic Cylinders
Proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial for the optimal performance and longevity of pneumatic cylinders and actuators. The first step in ensuring peak performance is selecting the appropriate air cylinder for the application. Prior to installation, it’s important to clean the mounting surface, fasten the cylinder securely, and align it properly with other components in the pneumatic system.
For maintenance, regularly inspect the cylinders for wear, damage, or leakage. Keep the cylinders clean and check the air supply system for proper pressure and cleanliness. Monitor the performance of the cylinders and consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for troubleshooting.
When working with air cylinders, it’s also important to follow safety precautions, such as wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), depressurizing the pneumatic system before performing any tasks, avoiding placing hands or any body parts between moving parts of the cylinder during operation, and adhering to all safety guidelines and instructions provided.
Actuation in Action
Recently, a major food and beverage manufacturer decided to make a change in their case rotator technology. The goal was to alleviate line of sight issues and simplify the design of the technology they were using on the factory floor.
The new case rotator actuation solution provided by Compact Automation’s pneumatic rotary actuators replaced a bulky, box-like design, eliminating the upper covering of the machine. This greatly reduced the number of components and complexity of the design while making operations safer by improving visibility for operators.







