Shorter Stroke Lengths Make LVDT Linear-Position Sensors Ideal for Hydraulic Cylinder Applications
By Michael Marciante, Applications Engineer, Macro Sensors
The development of computerized layer winding and improved microprocessing has considerably reduced the body length of the linear-position sensor compared to its measurable stroke length. With the improved stroke-to-length ratio (now up to 80%), the LVDT linear-position sensor becomes a viable position-measurement device for hydraulic cylinder positioning.
The role of the cylinder in most hydraulic applications is to move “something,” such as a valve, airplane tail rudder, or a boom or shovel on an off-road vehicle. In these applications, the control system needs a feedback device that tells it how far the cylinder or actuator moved to ensure proper operations. That’s where the linear-position sensor comes in. Installed within or outside the cylinder, the LVDT tracks the movement of actuators and reports data electronically to a control system that can monitor and provide alerts on operating conditions.
For example, if a pilot wants to turn the plane, he moves the joystick. The plane’s control system senses that he has moved the joystick and sends a signal to the tail rudder actuator to move the tail rudder. If the system has no way of knowing how far the actuator has moved through position feedback provided by an LVDT linear-position sensor, the plane could turn too much or not enough.
A second example would be a robotic arm. In this scenario, let’s say the robotic arm is going to move to pick up a piece of glass. If the control system does not know when to stop the arm by receiving position feedback from an LVDT linear-position sensor, the hydraulic cylinder could drive the arm right through the piece of glass.
Care should be taken in choosing the right LVDT linear-position sensor for an application. While miniature LVDTs are suitable for high-response dynamic measurement, hermetically sealed LVDTs are ideal for environments that experience high-pressure wash down, dust, and in some cases, submersion.
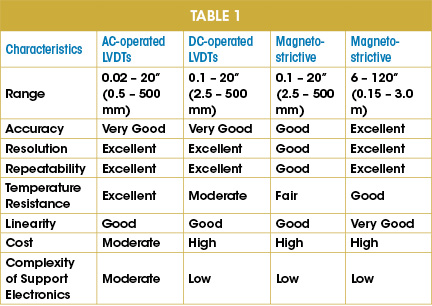
Many modern LVDTs can serve as cost-effective replacements for magnetostrictive technology that are somewhat more expensive over shorter ranges and have difficulty handling large shocks.
Table 1 compares the characteristics of LVDT linear-position sensors to magnetostrictive technology in different ranges.