ISO 4405 (Determination of Particulate Contamination by the Gravimetric Method)
By Sneha Swaminathan, Hollingsworth & Vose, and Susan Goldsmith, IBR Laboratories
This update is a technical summary of work done by the ISO 4405 (determination of particulate contamination by the gravimetric method) United States Technical Advisory Group to ISO/TC 131/SC 6 and participating U.S. laboratories.
Gravimetric Analysis
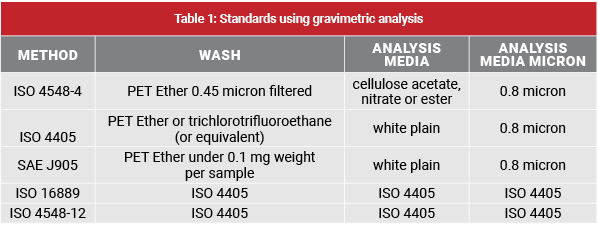
Gravimetric analysis is an important component of several standards (Table 1) for filter testing of lube, fuel and hydraulic filters to determine efficiency, life and verify system cleanliness. The general guidelines of the method are dependent on a number of factors, such as dust level, type and properties of solvent, membrane type and process conditions, such as drying time in oven, desiccator, and weighing. As with most methods, accuracy is dependent on the technique used, as well as on the materials and equipment used.
Interlab Study
To share best practices of ISO 4405 test technique, solvent, and membranes, seven U.S. laboratories met at IBR Laboratories in Michigan on 5th March 2018 for an interlab study. Filtered hydraulic fluid and dust suspension of 10 mg/l was given to each company. Each company representative demonstrated the company’s ISO 4405 technique for 20 minutes and shared the company’s procedure with the group.
Procedural Differences
Following the observation, discussion and brainstorming, major differences between the procedures of the participants were outlined as follows:
- type and volume of solvent used, which included one or a combination of solvents
- solvent to sample amount ratio
- type and material of membrane
- rinsing technique of the funnel and membrane
- drying time and time in desiccator
- drying temperature and membrane handling technique.
Some of the solvents used in the study included heptane, PET Ether, hexane, pentane, Bioact, isopropanol and d-limonene. The membrane types included polycarbonate, cellulose nitrate, mixed cellulose ester and polyethersulfone.
Continued Work of ISO 4405 Group
Each lab and company was comfortable with its solvent and technique for ISO 4405. Therefore, instead of specifying solvents, membranes and process conditions, the team wanted to suggest making ISO 4405 a more outcome-based method. We will develop informative recommendations for technique, solvents, and membranes. But these will not be normative (required).

Our work will focus on how to define the targets for an outcome-based method. The outcome based targets will include how to determine method detection limit (MDL), accuracy, precision, and range of usability as mg/L.
The ISO 4405 is used for determining mg/L in filter capacity and efficiency testing. Therefore, the MDL should be expressed as mg/L rather than mg. The MDL in this case is not affected by the instruments, since the specified balance limit of 0.01mg is much lower than the measured values. In this case, the detection limit is affected by sampling, sample volume, solvent, membrane, and technique.
For many labs at the meeting, this low limit was in the 2-5 mg/L range. This can have significant impact on calculated capacities for fuel and oil filter methods. The group will work on defining these parameters and acceptable ranges for given mg/L ranges.
If you are interested and would like to get involved in fluid power standards development, please contact Denise Husenica (dhusenica@nfpa.com) for more information.